WHEN TO USE THIS GUIDELINE
Use this guideline when chest pain suspected to be cardiac in origin
- After an initial clinical assessment fails to identify a more likely explanation for chest pain other than angina or acute myocardial infarction
- Do not use indiscriminately in all patients presenting with chest pain
Specific features of cardiac chest pain
- Site: central, retrosternal
- Character: pressure, heaviness, squeezing, burning (indigestion like)
- Radiation: arm(s), neck, jaw, gums
- Provoking factors: exercise, stress, cold temperature, lying down
- Relieving factors: rest, GTN
- Associated symptoms: nausea, sweating, breathlessness
- Duration: > 15 min
CLINICAL ASSESSMENT
- Perform 12-lead ECG on arrival. Repeat if further episodes of pain occur
- Advice in algorithm
Initial management of emergency presentation with suspected cardiac chest pain
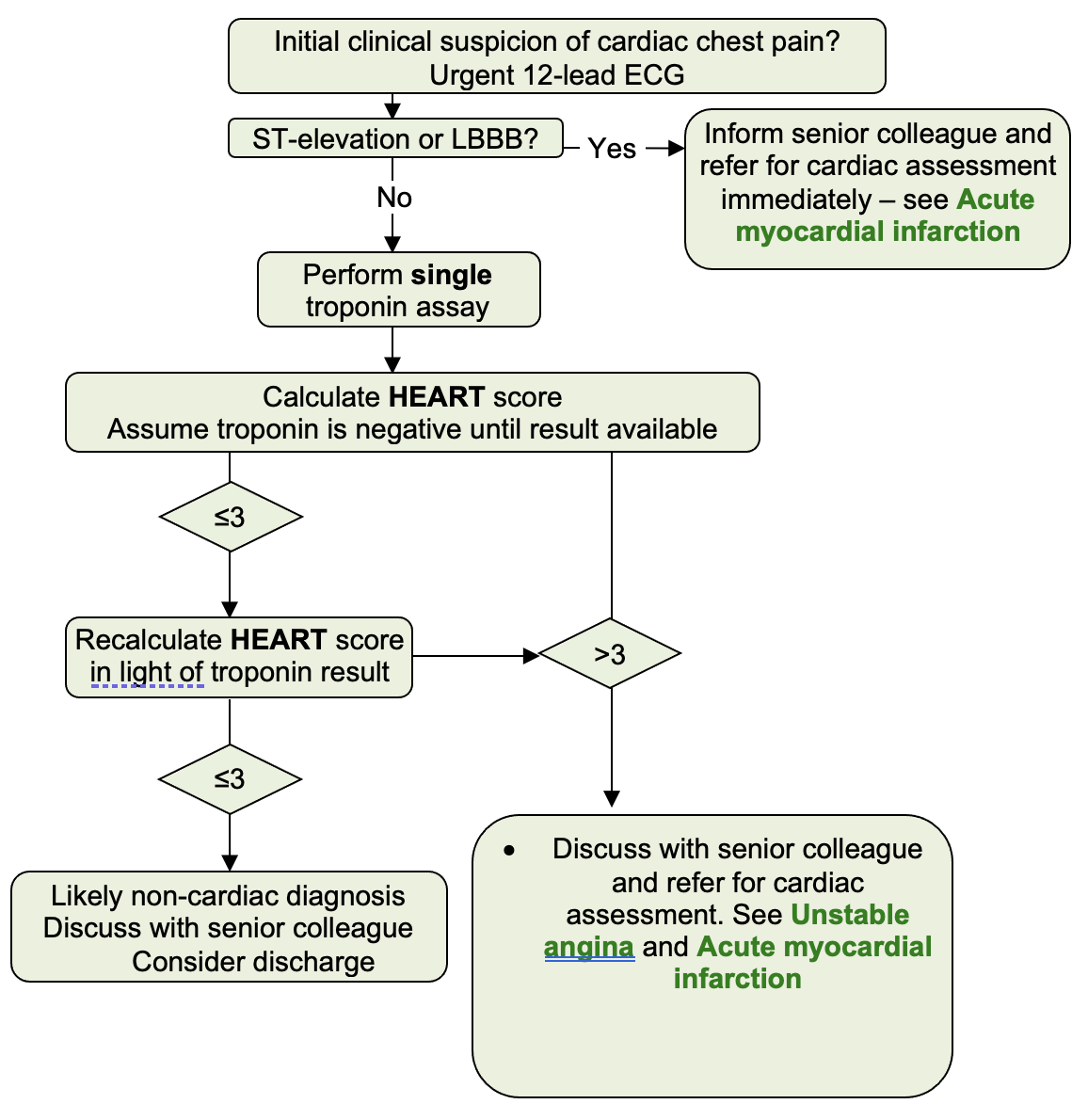
When troponin result available
- Recalculate HEART score
Score > 3
- Discuss with senior colleague and refer for cardiac assessment. See Unstable Angina and Acute myocardial infarction
Score ≤3
- Likely non-cardiac diagnosis
- Discuss with senior colleague
- Consider discharge
TREATMENT
- Aspirin 300 mg oral (chew and swallow)
- Glyceryl trinitrate 400 microgram/metered dose spray, 1–2 doses under tongue then close mouth
- Diamorphine – see Acute myocardial infarction guideline
DISCHARGE FROM EMERGENCY PORTAL
- Ensure patient is pain free
- Repeat ECG before discharge
- Request senior doctor review
- Complete discharge summary – inform GP of ECG and troponin I results
- Give patient an information sheet