RECOGNITION AND ASSESSMENT
Symptoms and signs
- Sudden onset, occasionally at rest
- Chest pain (unilateral)
- Dyspnoea
- Resonance on percussion with
- reduced vocal fremitus and
- reduced breath sounds if moderate-large
Patient in extremis
- If very dyspnoeic with circulatory compromise, and trachea or mediastinum (apex beat) displaced, consider TENSION PNEUMOTHORAX (very rare)
- give oxygen (10 L/min) through a high concentration (60–100%) mask
- insert a large bore cannula of at least 4.5 cm in length into second anterior intercostal space, midclavicular line
- then insert intercostal tube – see Intercostal tube drainage guideline
- Remove emergency cannula when bubbling in underwater seal system confirms intercostal tube system functioning
Investigations
- PA Chest X-ray
- measure interpleural (rim) distance at level of hilum
- If findings obscured by surgical emphysema or complex bullous disease, CT scan may help
- BEWARE: suspected basal pneumothorax usually implies a bulla. CT scan and previous chest X-rays will differentiate bullae from pneumothorax
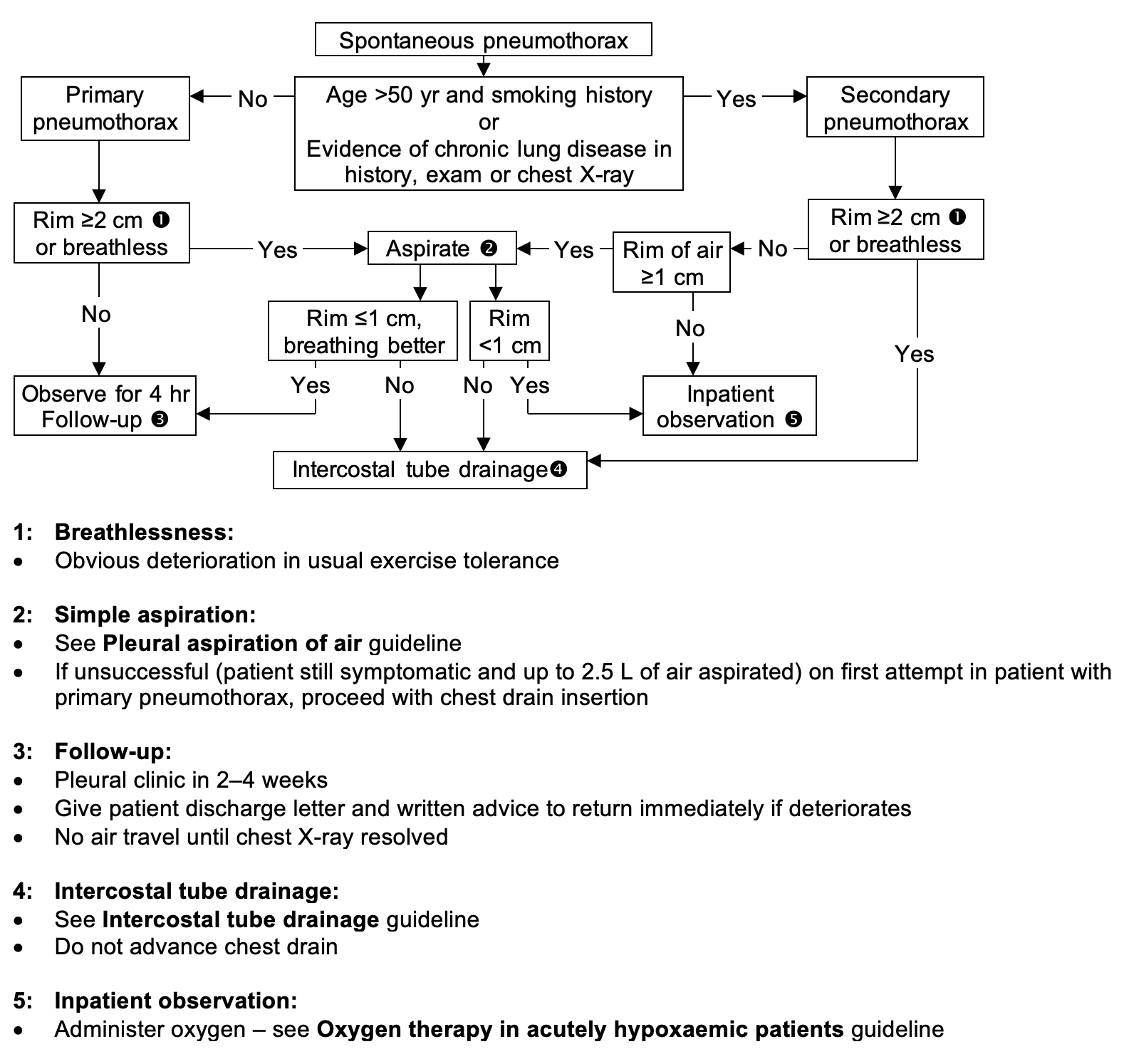
IMMEDIATE MANAGEMENT
- If bilateral or haemodynamically unstable, proceed to chest drain. See Intercostal tube drainage guideline
- Otherwise, follow guidance to help your decision
Guidance tool
SUBSEQUENT MANAGEMENT
Inpatient observation
- Admit to a Respiratory ward
- Administer oxygen – see Oxygen therapy in acutely hypoxaemic patients guideline
- Inpatient care until stable
Management of intercostal drains
- Always keep underwater seal below chest
- Do not clamp chest tube unless advised by pleural team or thoracic surgeon
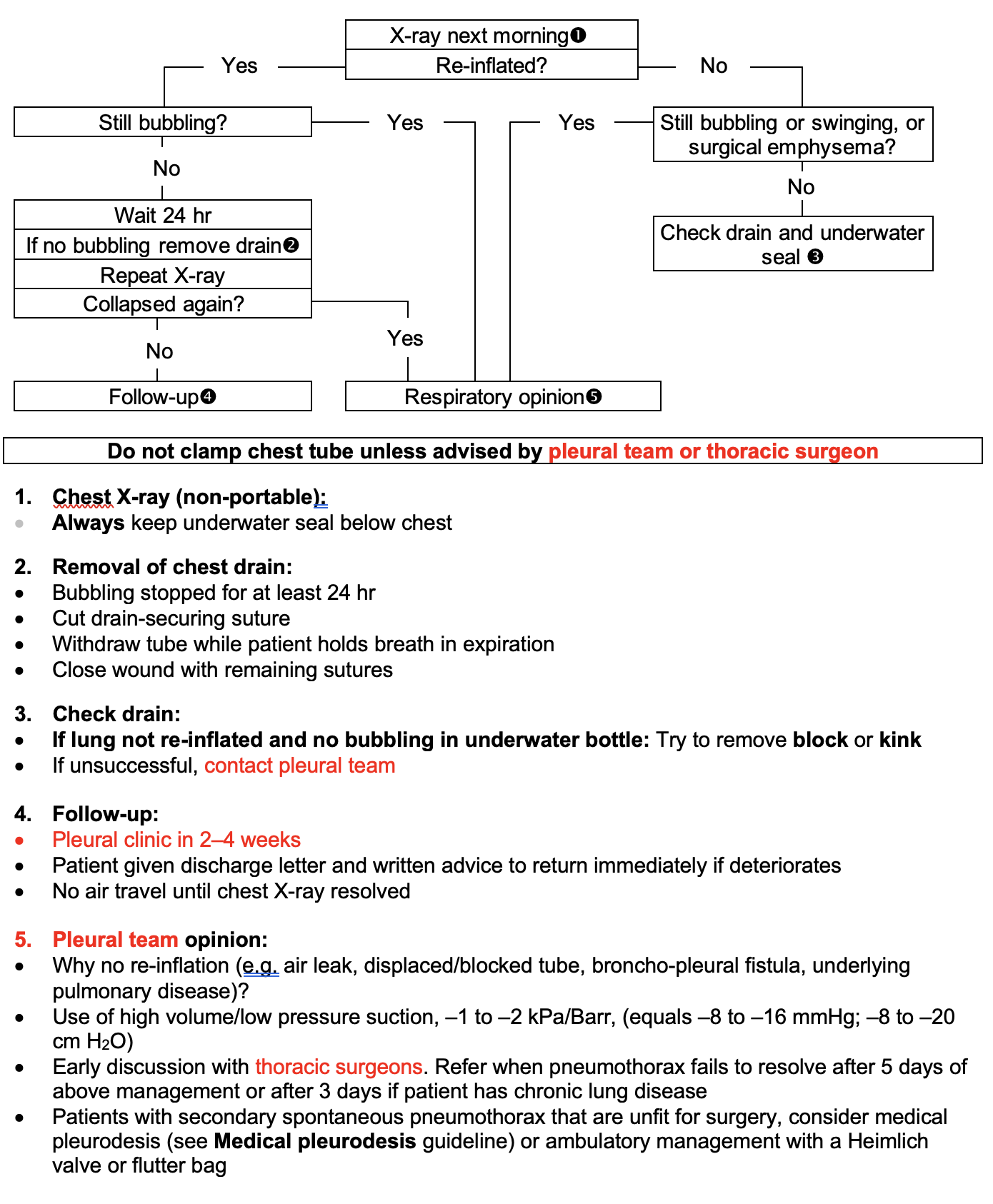
Repeat Chest X-ray
- On morning after insertion, repeat Chest X-ray (non-portable)
Result of repeat Chest X-ray
Guidance tool
REMOVAL OF CHEST DRAIN
- If bubbling stopped for at least 24 hr after lung re-inflated on Chest X-ray, remove drain
- If bubbling through underwater seal recurs in 24 hr after lung re-inflated on Chest X-ray, ask for pleural team opinion
How to remove
- Cut drain-securing suture
- Withdraw tube while patient holds breath in expiration
- If >12 French Gauge drain used, close wound with remaining sutures
- Repeat Chest X-ray
Recurrent pneumothorax
- If second or subsequent pneumothorax, restart Immediate management and refer to pleural team
DISCHARGE AND FOLLOW-UP:
- Arrange pleural clinic appointment in 2–4 weeks
- Give patient discharge letter and written advice to return immediately if deteriorates
- No air travel until full lung re-inflation on chest X-ray
© 2022 The Bedside Clinical Guidelines Partnership.
Created by University Hospital North Midlands and Keele University School of Computing and Mathematics.
Research and development team: James Mitchell, Ed de Quincey, Charles Pantin, Naveed Mustfa