RECOGNITION AND ASSESSMENT
Symptoms and signs
- Various CNS symptoms e.g. lethargy to coma and seizures
- Dehydration – hypovolaemia
- Those of underlying cause
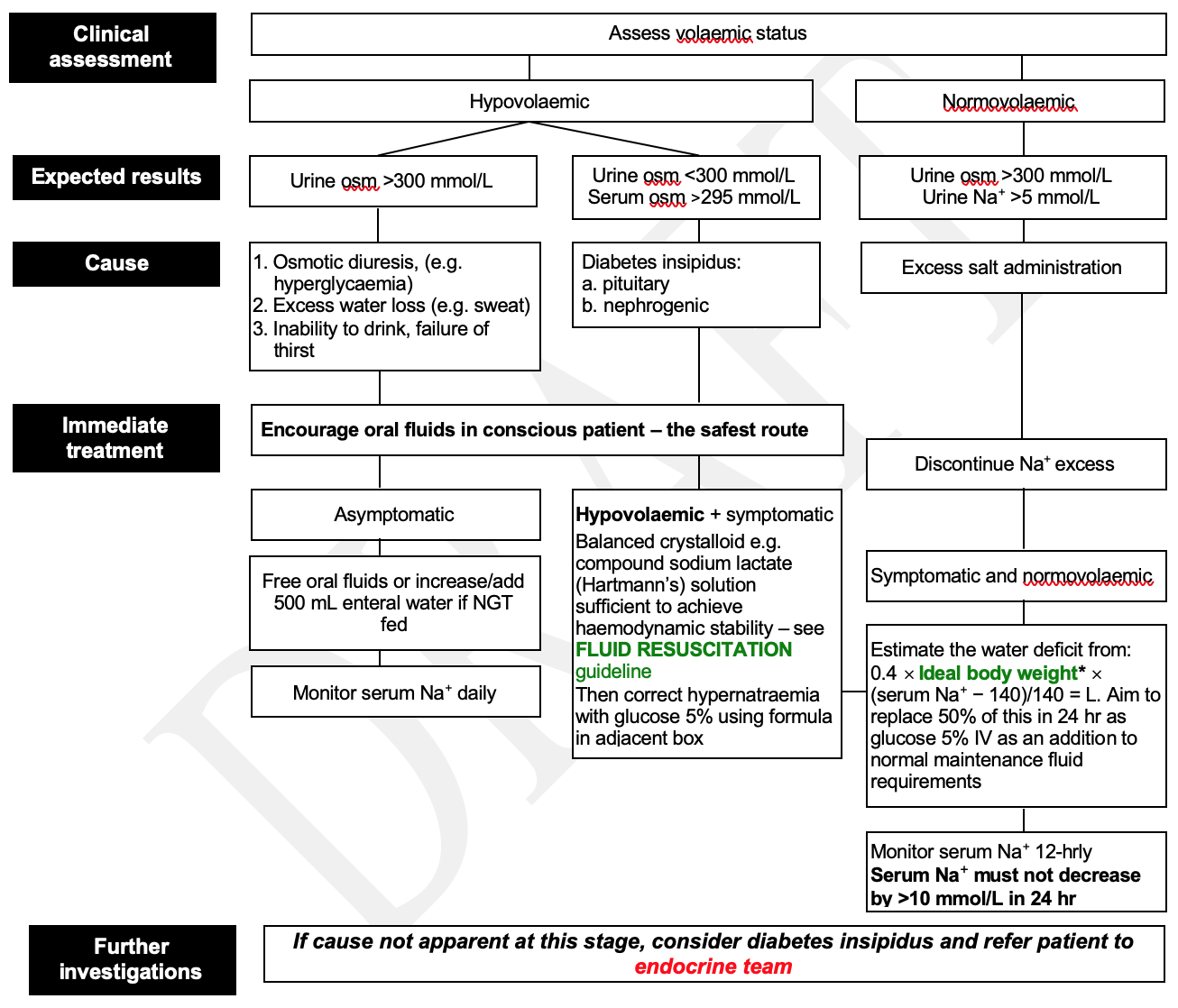
Clinical Assessment
- Assess volaemic status
Investigations
- Serum: U&E, glucose, osmolality
- Urine: U&E, osmolality
MANAGEMENT
- Treat the underlying cause. For guidance follow flowchart
- If cause still not apparent, consider diabetes insipidus and refer patient to endocrine team
Sodium Levels
- Rapid changes in sodium are more dangerous than HIGH Na+ ITSELF, even when the change is corrective
- Serum Na+ must not decrease by >10 mmol/L in 24 hr
Management flowchart tool